Dried Mango Fruit
11.00$ Original price was: 11.00$.8.00$Current price is: 8.00$.
- Extended 12-24 month shelf life with minimal storage requirements, offering year-round availability without seasonality concerns.
- Appeals to multiple consumer segments: health-conscious individuals, busy professionals seeking convenient snacks, and culinary enthusiasts.
- Strong market growth potential with 7.1% CAGR and rising demand for premium variants like organic and no-sugar-added options.
- Rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, providing strong marketing angles focused on health benefits.
- Available in various processing types and packaging formats to meet specific market demands and price points.
Description
Dried mango fruit has emerged as a popular snack option worldwide, combining the delicious tropical flavor of fresh mangoes with the convenience of extended shelf life. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of dried mango, from its nutritional benefits to production processes, market trends, and consumer applications. Dried mango is not only a delicious tropical treat but also a nutritional powerhouse that offers various health benefits, is available in multiple forms and processing types, and enjoys growing popularity in global markets as a healthy snacking alternative.
322952-31759_Soft Dried Mango (1)
Product Description and Varieties
Types of Dried Mango

Dried mango comes in several varieties to suit different consumer preferences and applications:
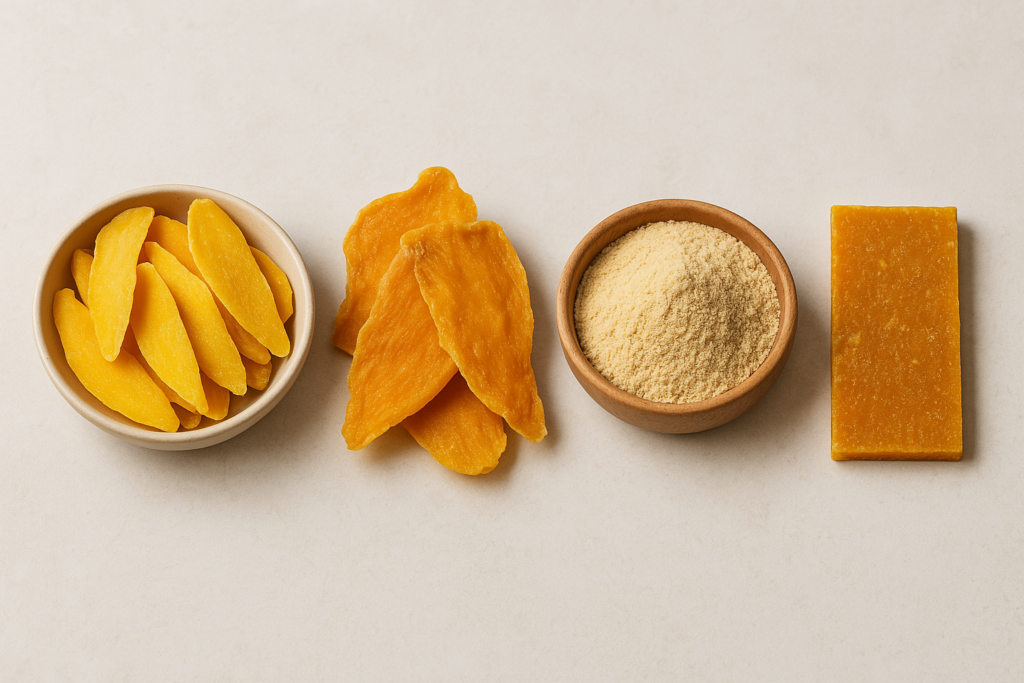
- Soft Dried Mango: Processed from selected fresh mangoes, typically from regions like the Mekong delta in Vietnam. It’s described as “chewy, tasty and naturally sweet”. This is one of the most popular forms and retains much of the original flavor profile of fresh mangoes.
- Freeze Dried Mango: Offers a different texture with maximum nutrient retention and a light, crispy feel. These typically command higher prices in the market.
- Conventional vs. Organic: Conventional dried mango is widely available, but organic versions produced without harmful pesticides and chemicals are gaining popularity for health-conscious consumers.
- No-Sugar-Added: These versions cater to health-conscious consumers looking to reduce sugar intake while still enjoying the natural sweetness of mangoes.
Forms and Processing Methods
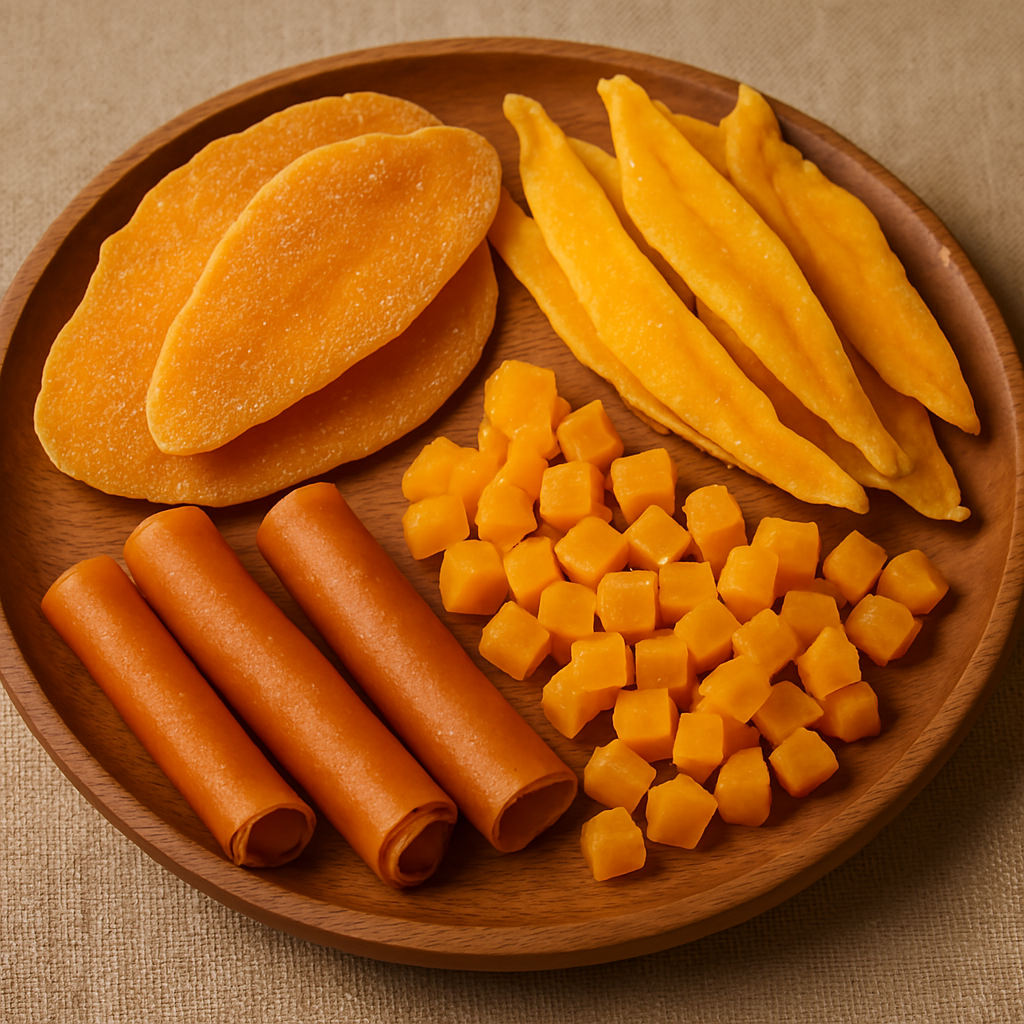
Dried mango is available in various physical forms:
- Slices: The most common form, with uniform thickness for consistent drying
- Chunks or Pieces: Larger, bite-sized pieces that provide a more substantial texture
- Powder: Finely ground dried mango used as an ingredient in various food products
- Fruit Bars: Compressed dried mango formed into convenient snack bars
Nutritional Benefits and Health Properties
Nutritional Profile
Dried mango is a nutrient-dense food that offers significant health benefits:
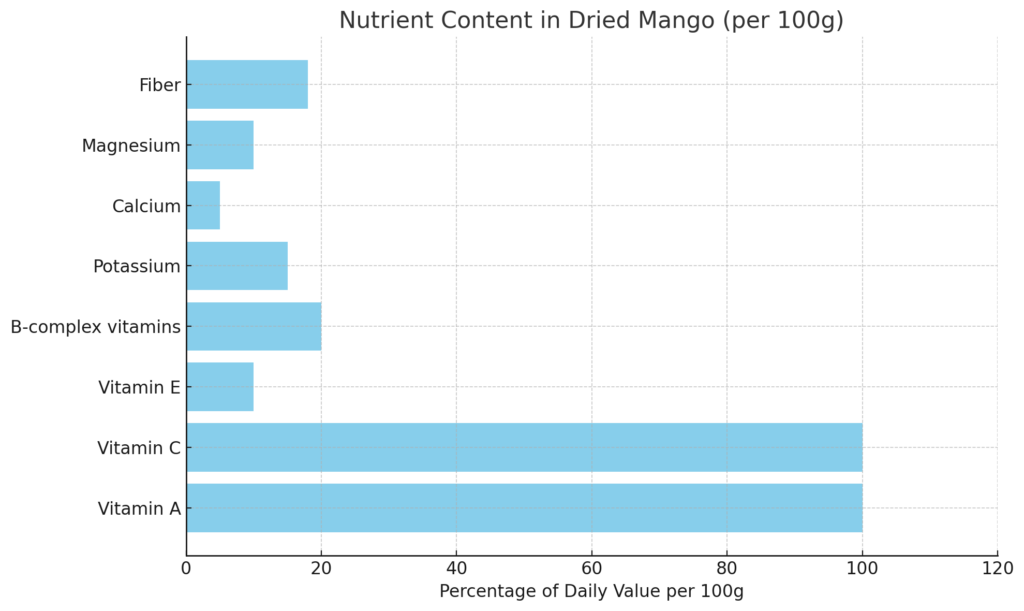
- Vitamins: Rich in vitamins A, C, E, and B-complex vitamins. 100 grams of mangoes can provide up to 100% of the daily requirement of Vitamin C and Vitamin A for an average person.
- Minerals: Contains important minerals including potassium, calcium, and magnesium that support various bodily functions.
- Fiber: High fiber content supports digestive health and helps prevent constipation.
- Antioxidants: Rich in polyphenols and other antioxidant compounds that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Specific Health Benefits
Research suggests that dried mango consumption may provide several health advantages:
- Digestive Health: The dietary fiber in dried mango supports the digestive system and helps prevent constipation.
- Immune Support: Rich vitamin C content helps boost the immune system.
- Energy Booster: Provides a quick source of carbohydrates and natural sugars for sustained energy.
- Skin Health: The vitamins and antioxidants in dried mango contribute to healthy skin.
- Heart Health: Potassium and magnesium help regulate blood pressure and enhance cardiovascular function.
Nutritional Information
A typical nutritional profile for dried mango (values may vary by processing method):
- Calories: 120-350 per serving
- Total Fat: 0g
- Sodium: 40-95mg
- Total Carbohydrate: 32-84g
- Dietary Fiber: 3-5g
- Total Sugars: 28-63g (may include added sugars in some products)
- Protein: 1g or less
For a 40-gram serving (about 1/4 cup), dried mango typically contains approximately 128 calories, 31 grams of carbohydrates, 1 gram of fiber, 27 grams of sugar, and 1 gram of protein, with 19% of the Daily Value (DV) for vitamin C, 7% DV for folate, and 3% DV for vitamin A.
Production Process and Technology
From Fresh Fruit to Dried Product
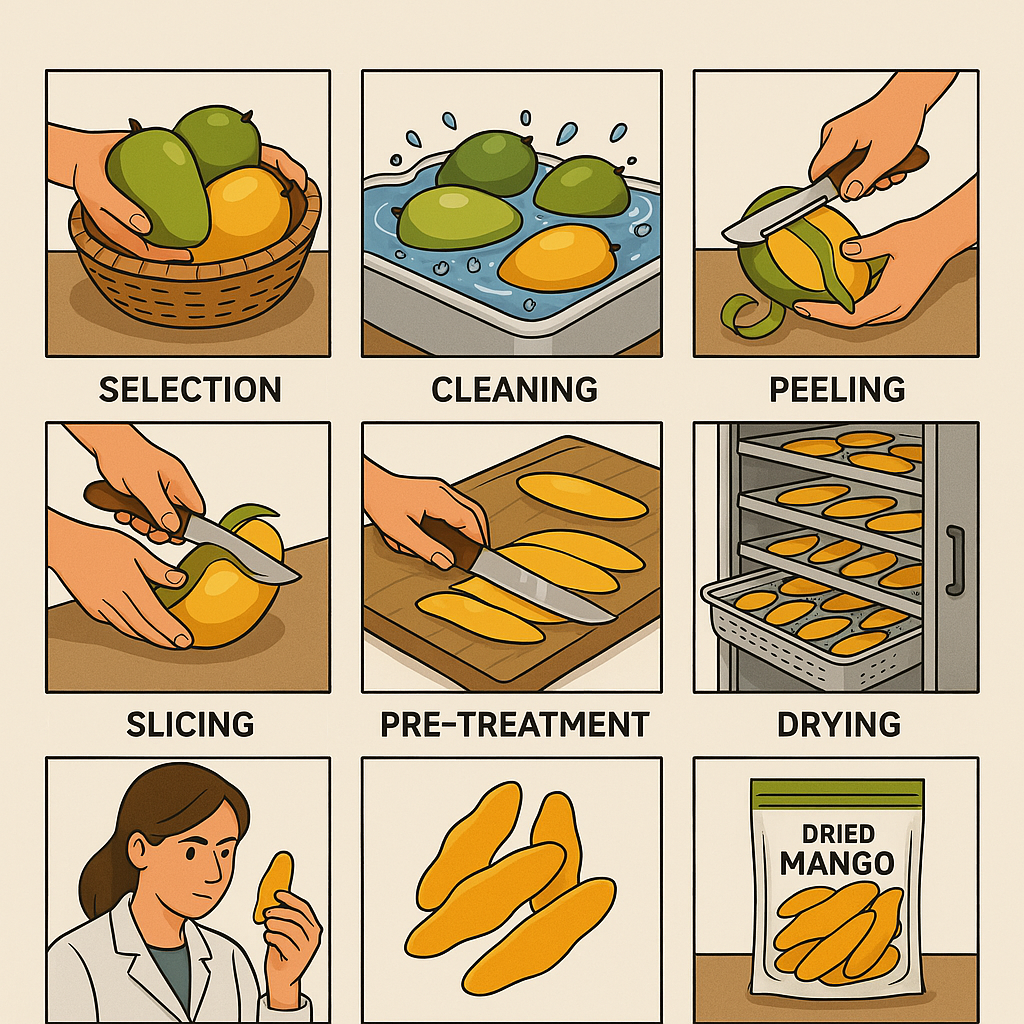
The production of dried mango follows a systematic process to ensure quality and food safety:
- Selection of Mangoes: Careful selection of ripe, high-quality mangoes at peak flavor. Common varieties include Keo (Vietnam), Haden, Tommy Atkins, and Kent.
- Cleaning and Washing: Thorough washing to remove dirt, debris, and any pesticide residues.
- Peeling and Pitting: Removal of skin and seed to prepare the fruit for slicing.
- Slicing: Cutting the mango into uniform pieces to ensure even drying. Thickness may vary based on desired final texture.
- Pre-Treatment: Often involves blanching, steam treatment, or dipping in a citric acid solution to maintain color and prevent spoilage.
- Drying Process: The critical step where moisture is removed while preserving nutrients and flavor.
- Quality Control: Checking for proper moisture content, color, taste, and safety parameters.
- Packaging: Sealing in appropriate packaging materials to maintain freshness and extend shelf life.
Advanced Drying Technologies
Several drying technologies are employed in commercial dried mango production:
- Heat-Pump Drying System: Low-temperature drying technology that helps retain maximum nutrients and natural flavors.
- Infrared Drying: Provides efficient moisture removal while maintaining product quality.
- Solar Dryers: More traditional and environmentally friendly option utilized in some producing regions.
- Dehydrators: Controlled environment machines that provide consistent results for commercial production.
The Science Behind Drying
The drying process typically involves hot air drying, where warm, low-moisture air evaporates surface water, and diffusion draws internal moisture to the surface. This method can lead to case-hardening at high temperatures, forming a hard outer layer that traps moisture, potentially causing spoilage. The process breaks down the cellular structure, causing shrinkage, and is a major method for ensuring shelf stability of the product.
Comparison with Fresh Mango
Compared to fresh mango, dried mango has concentrated sugars and calories due to water removal. For instance, a one-third cup of dried mango (about 53 grams) contains around 160 calories, mostly from carbohydrates, while fresh mango (165 grams or 1 cup) provides 67% DV for vitamin C but fewer calories. The drying process reduces vitamin C content, with dried mango carrying only a fraction compared to fresh, but it retains significant fiber and antioxidants.
Fresh mango is seasonal and juicy, ideal for salads and smoothies, while dried mango offers year-round convenience, with higher fructose levels best consumed in the morning or on-the-go, not late at night. Each form has its own culinary applications and nutritional advantages.
Market Information and Trends
Global Market Overview
The dried mango industry shows strong growth potential and evolving consumer preferences:
- Market Size: The global dried mango market was estimated to be worth billions of dollars in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% anticipated throughout the projection period.
- Growth Drivers: Increasing demand for healthy snacking options, growing popularity among those choosing vegan and vegetarian diets, and successful marketing initiatives highlighting nutritional benefits.
- Price Range: Wholesale prices vary considerably based on quality, certification, and processing method.
Sustainability and Consumer Preferences
Environmental and ethical considerations are increasingly important in the dried mango market:
- Organic Certification: Growing demand for organically produced dried mango, especially in European markets.
- Fair Trade: Fair trade certification is becoming an important marketing strategy, particularly in Germany and other European countries.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Various sustainability programs being implemented in dried mango production countries to meet consumer expectations.
- Reduced Sugar Options: Increasing preference for no-sugar-added varieties as consumers become more health-conscious.
Packaging, Storage, and Applications
Packaging Solutions
Proper packaging is crucial for maintaining dried mango quality:
- Materials: Common packaging materials include PE bags, cartons, glass jars, and aluminum lid plastic cans.
- Barrier Properties: Effective packaging should provide moisture, oxygen, and light barriers to prevent quality degradation.
- Sizing Options: Available in various sizes from 120g-300g for retail to 500g-10kg for commercial use.
- Requirements: Food-grade, heat-sealable, and durable materials are essential for quality packaging.
Storage Recommendations
To maintain optimal quality:
- Environment: Store in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Shelf Life: Typically ranges from 12 to 24 months when properly stored.
- After Opening: Resealable packaging helps maintain freshness once opened.
Common Applications
Dried mango is versatile and used in various food applications:
- Direct Consumption: Popular as a convenient, healthy snack.
- Culinary Ingredient: Used in baking, confectionery, and dessert preparations.
- Breakfast Foods: Common addition to breakfast cereals and muesli mixes.
- Food Service: Growing use in food service applications and prepared foods.
Creative Culinary Uses
Beyond snacking, dried mango can be used in various recipes:
- Baked goods such as mango squares or scones
- Trail mixes combining dried mango with nuts and seeds
- Toppings for cereals, oatmeal, and yogurts
- Savory dishes like curries or chutneys
- Energy balls and homemade granola bars
- Infused teas and beverages
Health Considerations
Benefits Supported by Research
Scientific studies support several health benefits of dried mango:
- Rich vitamin C content promotes healthy skin and a strong immune system by acting as an antioxidant, potentially reducing cell damage and chronic disease risk.
- Vitamin A and folate support eye health and DNA synthesis.
- Dietary fiber improves gut health, with studies linking it to higher diet quality and lower body weight.
- Antioxidants like polyphenols and carotenoids may reduce risks of diabetes, cancer, and inflammation.
Considerations for Consumption
Despite its benefits, certain considerations should be kept in mind:
- High calorie and sugar content necessitate moderation, especially for those with high blood sugar or diabetes.
- Sweetened versions have more added sugars, so choosing unsweetened options is advisable for those monitoring sugar intake.
- Potential allergies to profilin or urushiol compounds in mangoes may affect some individuals.
- Some products contain preservatives like sodium bisulfite, which may cause reactions in sulfite-sensitive individuals, particularly those with asthma.
Availability and Purchasing
Dried mango is widely available at major retailers, specialty food stores, and online marketplaces. Prices vary by brand, processing type, and whether the product is organic or conventional. Unsweetened and organic varieties typically command higher prices but offer benefits for health-conscious consumers.
When purchasing dried mango, consider factors such as:
- Added sugars (check ingredients list)
- Processing method (freeze-dried vs. conventional drying)
- Organic certification
- Country of origin
- Packaging quality for freshness
Conclusion
Dried mango fruit represents a successful intersection of taste, nutrition, and convenience in today’s food market. Its rich nutritional profile, including vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, makes it an attractive option for health-conscious consumers. The variety of available forms, processing methods, and formulations allows it to serve diverse market segments and culinary applications.
The industry continues to evolve with growing emphasis on sustainability, organic certification, and reduced sugar options. As production technologies advance and consumer awareness of the benefits increases, dried mango is likely to maintain its strong growth trajectory in the global dried fruit market.
For consumers, understanding the nutritional benefits, production processes, and market trends associated with dried mango can help inform purchasing decisions and healthy consumption habits in this dynamic and growing sector.
Reviews (0)
Chưa có bình luận nào



Đánh giá sản phẩm
There are no reviews yet.