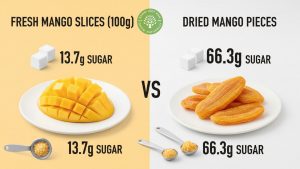
Dried mango sugar content is significantly higher than fresh mango, with approximately 66.3 grams of sugar per 100 grams compared to just 13.7 grams in fresh fruit. At Ogani VN, we understand your concerns about sugar intake while still wanting to enjoy this tropical delicacy.
Why dried mango sugar levels are so high
When mangoes undergo the dehydration process, their natural sugars become concentrated as water is removed. This concentration process transforms a moderately sweet fresh fruit into a sugar-dense snack. A single ounce of dried mango sugar contains roughly 18 grams of sugar, which equals about 4.5 teaspoons.
The sugar in dried mango comes primarily from fructose, the natural fruit sugar that gives mangoes their characteristic sweetness. Unlike processed foods with added sugars, dried mango retains its natural sugar profile, though in much higher concentrations. This natural fructose provides quick energy but can also cause blood sugar spikes if consumed in large quantities.
Commercial dried mango products often contain additional sweeteners beyond the fruit’s natural sugars. Many manufacturers add cane sugar, corn syrup, or artificial sweeteners to enhance flavor and extend shelf life. At Ogani VN, we recommend checking ingredient labels carefully to distinguish between naturally occurring and added sugars.
Health effects of dried mango sugar consumption
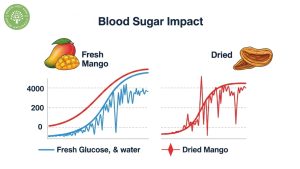
Blood sugar impact and diabetes considerations
The high dried mango sugar content can significantly affect blood glucose levels. People with diabetes or prediabetes should monitor their intake carefully, as the concentrated fructose can cause rapid blood sugar elevation. Unlike fresh mango, which contains more fiber and water to slow sugar absorption, dried mango delivers sugar more quickly to your bloodstream.
The glycemic index of dried mango is considerably higher than its fresh counterpart. This means your body processes the sugars more rapidly, potentially leading to energy crashes after the initial sugar high. For individuals managing blood sugar levels, portion control becomes crucial when enjoying this tropical treat.
Nutritional benefits beyond sugar content
Despite concerns about dried mango sugar levels, this fruit offers valuable nutrients. Each serving provides vitamin C, supporting immune function and collagen production. The potassium content helps regulate blood pressure and supports heart health. Additionally, dried mango contains dietary fiber, though less than fresh fruit due to processing methods.
Antioxidants like beta-carotene remain present in dried mango, contributing to eye health and immune support. These compounds help protect cells from oxidative stress and may reduce inflammation. The vitamin A content supports skin health and proper vision function.
Managing dried mango sugar intake effectively

Portion control and moderation guidelines
Effective dried mango sugar management starts with understanding appropriate serving sizes. A standard serving equals about 1/4 cup or roughly 40 grams, containing approximately 26 grams of sugar. This represents nearly your entire daily recommended sugar intake from one small portion.
We recommend treating dried mango as an occasional treat rather than a daily snack. Limiting consumption to 2-3 times per week helps maintain nutritional balance while satisfying sweet cravings. When you do indulge, pair dried mango with protein or healthy fats to slow sugar absorption and reduce blood glucose spikes.
Consider using dried mango as a natural sweetener in recipes rather than eating it plain. Adding small amounts to yogurt, oatmeal, or trail mix provides sweetness while distributing the sugar content across a more balanced meal. This approach helps minimize the concentrated sugar impact while maximizing flavor.
Choosing healthier dried mango options

Look for unsweetened varieties when shopping for dried mango products. These options contain only the fruit’s natural sugars without additional sweeteners. While still high in dried mango sugar, they provide better nutritional value than heavily processed alternatives.
Organic dried mango typically undergoes less processing and contains fewer preservatives. Some brands offer low-sugar versions that use different drying techniques to reduce overall sugar concentration. At Ogani VN, we stock various options to meet different dietary preferences and health goals.
Comparing dried mango sugar to other sweeteners
Fresh mango contains significantly less sugar than its dried counterpart, making it a better choice for sugar-conscious consumers. When comparing dried mango sugar to processed sweeteners, dried mango provides additional nutrients like vitamins and minerals that refined sugar lacks entirely.
Honey and maple syrup contain similar sugar levels to dried mango but offer different flavor profiles and nutritional benefits. Table sugar delivers pure sucrose without any accompanying nutrients, while dried mango provides fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins alongside its natural sugars.
The advantage of dried mango sugar lies in its natural origin and nutrient density compared to artificial sweeteners. However, its concentrated nature means even small portions deliver substantial sugar loads, requiring careful consumption planning for optimal health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much dried mango is safe to eat daily? Limit dried mango to 1-2 pieces (about 20-30 grams) per day to manage sugar intake effectively while still enjoying its benefits.
Is dried mango healthier than candy? Yes, dried mango provides vitamins, minerals, and fiber that candy lacks, though both are high in sugar and should be consumed moderately.
Can diabetics eat dried mango? Diabetics should consult healthcare providers before consuming dried mango due to its high sugar content, which can significantly impact blood glucose levels.
Does no-sugar-added dried mango contain sugar? Yes, no-sugar-added varieties still contain the fruit’s natural sugars, typically around 60-70% of regular dried mango’s sugar content.
How does dried mango sugar compare to table sugar? Dried mango contains natural fructose plus small amounts of glucose and sucrose, while table sugar is pure sucrose. Both affect blood sugar, but dried mango provides additional nutrients.
Making informed choices about dried mango sugar
Understanding dried mango sugar content empowers you to make informed dietary choices. While this tropical fruit offers nutritional benefits, its concentrated sugar levels require mindful consumption. By practicing portion control and choosing quality products, you can enjoy dried mango as part of a balanced diet.
Ready to explore healthier dried fruit options? Visit Ogani VN‘s collection of premium, naturally processed dried fruits that prioritize quality and nutritional value. Contact our nutrition specialists today for personalized recommendations that align with your health goals and dietary requirements.
Read more:
-
- Are Dry Mangoes Healthy? The Complete Truth About This Sweet Snack
- What Is Soft Dried Fruit? Process, Moisture Level & Why It’s Different
- Are Dried Mango Slices Healthy? Complete Nutrition Guide 2025
- 20 Soft Dried Fruit Kid Snacks for Lunchboxes & Travel
- Dried Mango Health Benefits: Complete Guide To Nature’s Sweet Superfruit